Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence: Enabling Early Warning of Soil Salinization
土壤盐渍化,是指土壤底层或地下水中的可溶性盐分随水分上升至地表,水分蒸发后,盐分在表层土壤中积累的过程。这就像海水晒盐一样,水分被“晒干"了,盐分却留了下来。土壤盐渍化是影响农业生产和生态健康的全球性问题。
Soil salinization refers to the process in which soluble salts from the soil subsurface or groundwater migrate upward with water to the soil surface. After the water evaporates, the salts accumulate in the topsoil. This is similar to sea salt production: the water is "dried out," but the salts remain. Soil salinization is a global issue affecting agricultural production and ecological health.

土壤盐渍化 / Soil Salinization
盐胁迫的负面影响主要体现在四个方面:
·水分亏缺与渗透胁迫:土壤盐分升高导致水势降低,阻碍根系吸水,引发渗透胁迫,造成植株生理缺水。
·离子毒害:过量钠离子和氯离子侵入细胞,破坏膜结构和酶活性,干扰正常代谢。
·氧化胁迫:盐诱导活性氧(ROS)大量产生,引发膜脂过氧化,细胞结构受损,丙二醛(MDA)含量上升。
·光合作用抑制:盐胁迫降低叶绿素含量、改变色素组成,直接削弱光系统II(PSII)效率,抑制光合碳同化。
The negative impacts of salt stress are mainly manifested in four aspects:
·Water Deficit and Osmotic Stress: Increased soil salinity lowers water potential, hindering water uptake by roots and causing osmotic stress, which leads to physiological water deficiency in plants.
·on Toxicity: Excessive sodium and chloride ions enter cells, disrupting membrane structures and enzyme activity, thereby interfering with normal metabolic processes.
·Oxidative Stress: Salt stress induces the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), triggering membrane lipid peroxidation, damaging cell structures, and increasing malondialdehyde (MDA) content.
·Inhibition of Photosynthesis: Salt stress reduces chlorophyll content, alters pigment composition, directly impairs the efficiency of photosystem II (PSII), and suppresses photosynthetic carbon assimilation.
其中,光合作用的变化尤为关键。而日光诱导叶绿素荧光(SIF)作为光合作用的“副产物",能够灵敏地捕捉到盐胁迫下光合机构的早期响应。
例如,受盐胁迫的植物叶片往往出现叶绿素含量下降、光合活性会下降,SIF信号也随之减弱,这种变化比传统的植被指数(如NDVI)更早、更灵敏,因为植被指数通常反映的是冠层结构或色素含量的变化,而这些变化往往在胁迫发生一段时间后才显现。
Among these, changes in photosynthesis are particularly critical. As a byproduct of photosynthesis, sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) can sensitively capture the early responses of the photosynthetic apparatus under salt stress.
For example, salt-stressed plants often exhibit decreased chlorophyll content and reduced photosynthetic activity, accompanied by a decline in SIF signals. These changes occur earlier and are more sensitive than traditional vegetation indices (such as NDVI), as vegetation indices typically reflect alterations in canopy structure or pigment content, which often become apparent only after the stress has persisted for some time.
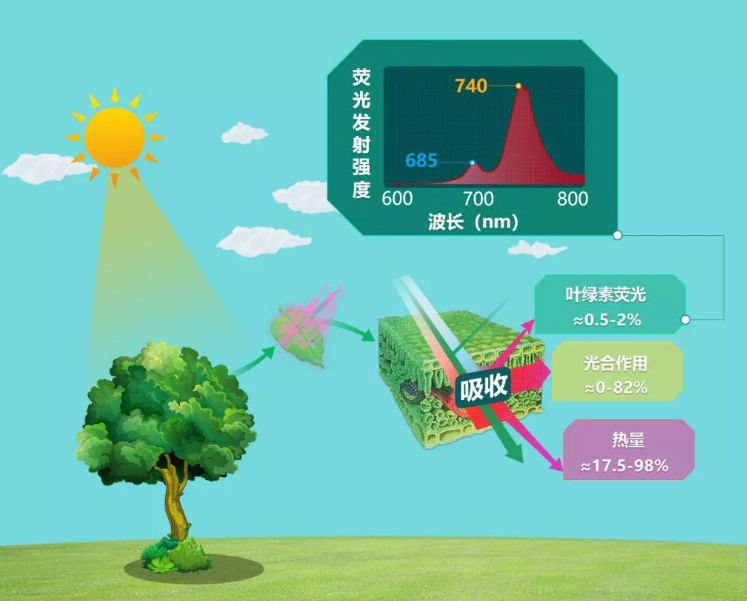
日光诱导叶绿素荧光的产生 / Generation of Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence
西北农林科技大学基于全球OCO-2的SIF产品(GOSIF)的SIF观测时间序列(2000 ∼ 2020)的标准化日致叶绿素流失指数(SIFI)来建立土壤盐度模型。下图是该课题组得出的SIF观测对土壤盐度估算的评价。
Using the standardized SIF-based loss index (SIFI) derived from the global OCO-2 SIF product (GOSIF) time series (2000–2020), researchers from Northwest A&F University developed a model for estimating soil salinity. The figure below shows the evaluation of SIF observations for soil salinity estimation by this research team.
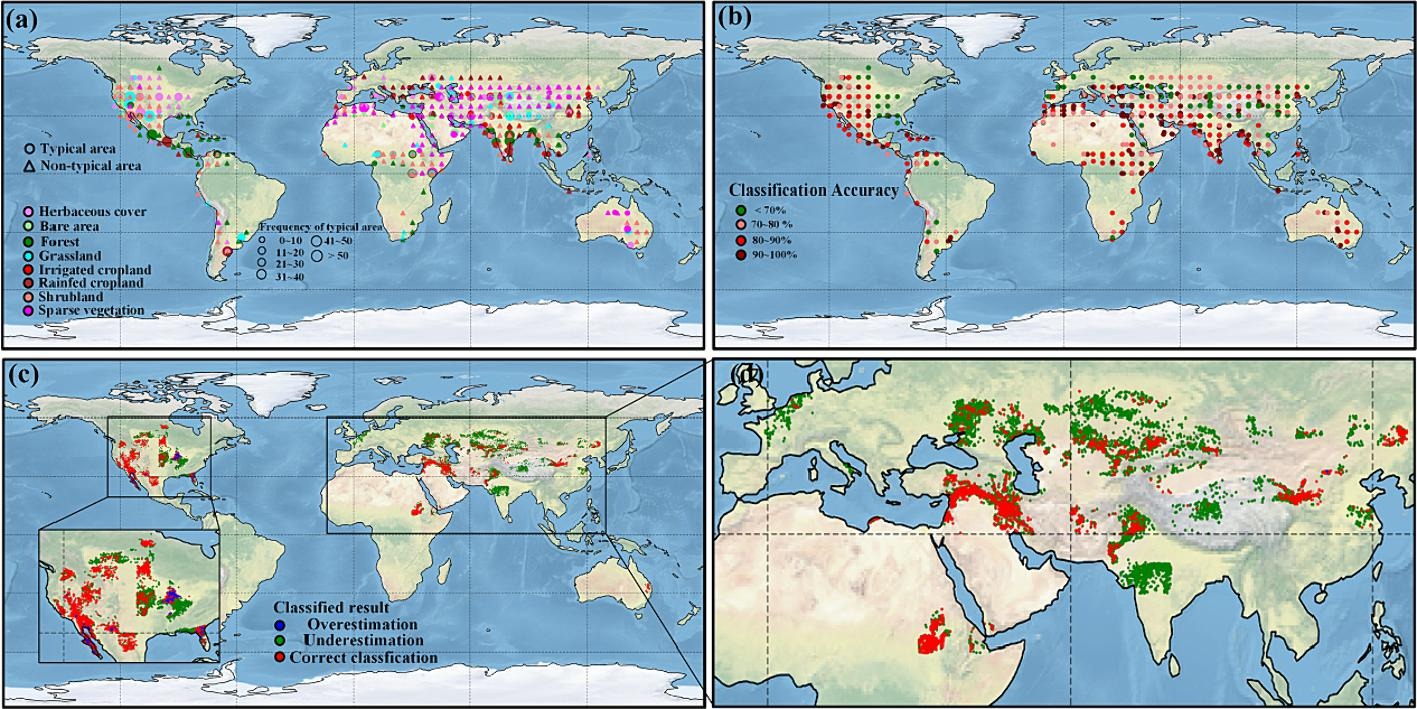
(a)是典型区域和非典型区域的分布;(b)是SIF观测对受盐影响土壤的分类精度;(c)∼(d)为SIF观测的分类结果。
(a) Distribution of typical and atypical regions; (b) Classification accuracy of SIF observations for salt-affected soils; (c)‒(d) Classification results based on SIF observations.
新疆的科研机构也利用日光诱导叶绿素荧光来捕捉新疆和中亚地区的植物对盐胁迫的反应。
Research institutions in Xinjiang have also utilized sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence to monitor plant responses to salt stress in Xinjiang and Central Asia.
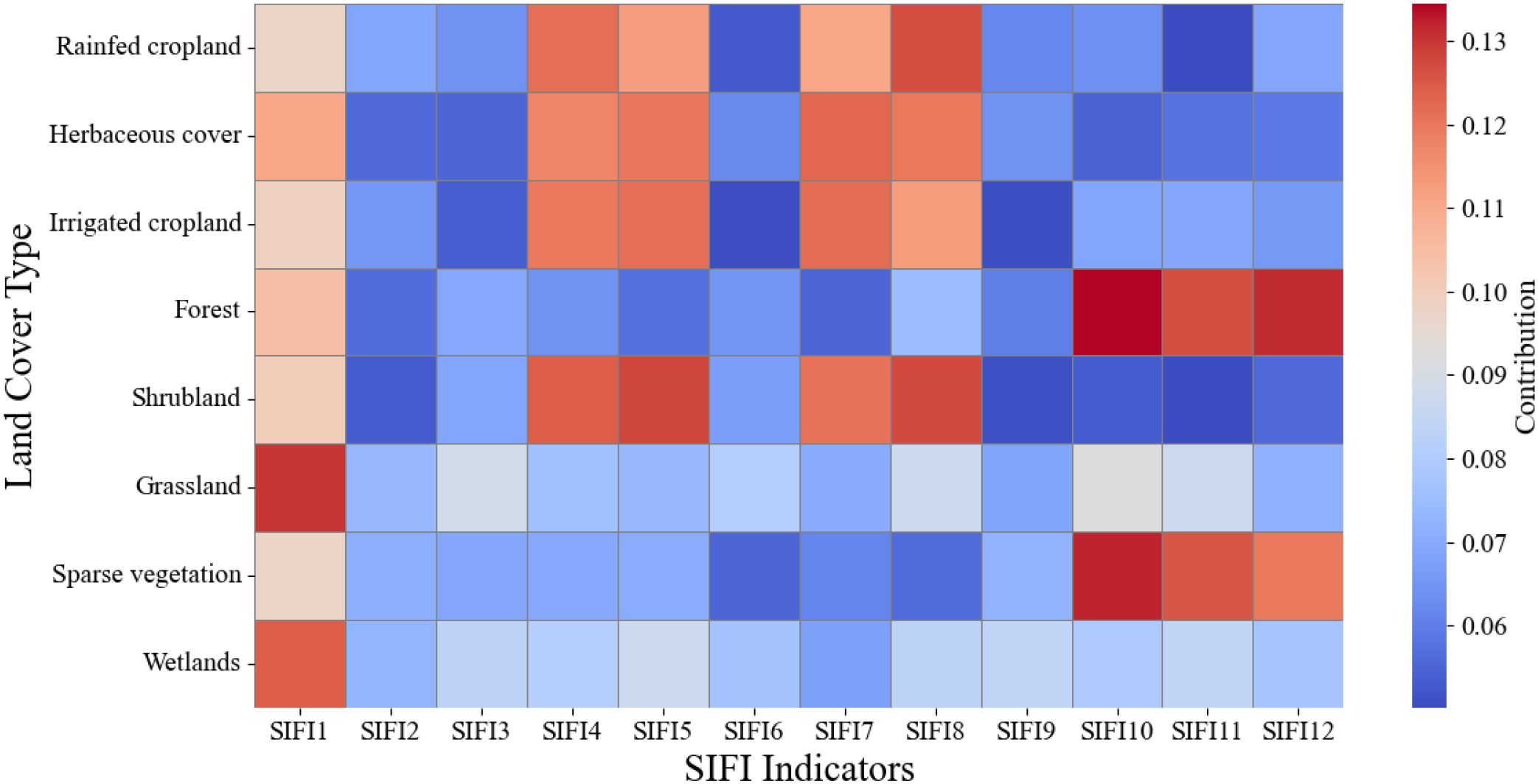
标准化 SIFI 指标对八种代表性土地覆盖类型的相对建模贡献
Relative modeling contributions of the standardized SIFI indicator for eight representative land cover types.
SIF对早期胁迫的高度敏感性,使其成为监测盐胁迫的有效工具,主要体现在以下方面:
·早期预警与精准管理:SIF可实现早期胁迫区域识别,帮助管理者及时调整灌溉、施用土壤改良剂或更换耐盐品种,减轻产量损失。
·耐盐品种选育:通过无损监测不同品种在盐条件下的响应,可高效筛选出光合效率稳定的耐盐材料,加速抗逆育种进程。
·科学研究与模型融合:SIF可与多源遥感数据及生态模型(如SCOPE、VISIT-SIF)结合,深化盐胁迫下作物生理响应机制的认识,推动胁迫生理学发展。
The high sensitivity of SIF to early-stage stress makes it an effective tool for monitoring salt stress, mainly demonstrated in the following aspects:
·Early Warning and Precision Management: SIF enables the identification of stress-affected areas at an early stage, helping managers adjust irrigation, apply soil amendments, or switch to salt-tolerant varieties in a timely manner to mitigate yield losses.
·Breeding Salt-Tolerant Varieties: By non-destructively monitoring the responses of different varieties under saline conditions, photosynthetically efficient and salt-tolerant materials can be efficiently screened, accelerating the process of stress-resistant breeding.
·Scientific Research and Model Integration: SIF can be integrated with multi-source remote sensing data and ecological models (e.g., SCOPE, VISIT-SIF) to deepen the understanding of crop physiological responses under salt stress and advance stress physiology research.
目前,SIF的监测已从实验室走向田间实际应用。
以我司推出的系列日光诱导叶绿素荧光监测系统为例,用户无需自行搭建复杂模型与反演流程,即可直接获取精准的SIF产额及光合作用效率数据。
我们提供多种部署形态:在线式监测系统可安装于地面塔台,实现无人值守、连续监测并自动回传数据至云平台;无人机载系统则支持灵活机动、高空间分辨率的田间巡测。无论哪种方式,都能帮助用户快速、定量地评估盐胁迫对植物光合功能的具体抑制程度,为精准农业提供稳定可靠的数据底层。
Currently, SIF monitoring has transitioned from the laboratory to practical field applications.
For instance, our company's series of sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence monitoring systems allow users to directly obtain accurate SIF yield and photosynthetic efficiency data without the need to build complex models or inversion processes.
We offer multiple deployment options: online monitoring systems can be installed on ground-based towers for unattended, continuous monitoring with automatic data transmission to cloud platforms; UAV-mounted systems support flexible, high-spatial-resolution field surveys. Both approaches help users quickly and quantitatively assess the extent of salt stress-induced inhibition of plant photosynthetic function, providing a stable and reliable data foundation for precision agriculture.

ABN-SIF系列 / ABN-SIF Series
总之,日光诱导叶绿素荧光技术为盐渍化监测与管理提供了强有力的工具。它早期、灵敏反映光合生理变化,支持精准农业、耐盐育种与大尺度生态监测,为保障粮食安全提供重要科技支撑。
In summary, sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence technology provides a powerful tool for monitoring and managing soil salinization. It offers early and sensitive detection of photosynthetic physiological changes, supports precision agriculture, salt-tolerant breeding, and large-scale ecological monitoring, and delivers crucial technological support for ensuring food security.
案例来源 / Sources :
1. Du, R., Xiang, Y., Chen, J., Lu, X., Wu, Y., He, Y., Xiang, R., Zhang, Z., & Chen, Y. (2024). Potential of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) to access long-term dynamics of soil salinity using OCO-2 satellite data and machine learning method. Geoderma, 444, 116855.
2. Cui, K., Ding, J., Wang, J., Tan, J., Han, L., & Li, J. (2025). Potential of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence for monitoring long-term dynamics of soil salinity in Central Asia the Xinjiang Region China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 16.
 客服热线:400-688-7769
客服热线:400-688-7769 邮箱:market@exponentsci.com
邮箱:market@exponentsci.com 固话:020-89858550
固话:020-89858550 地址:广州市天河区广汕二路602号惠诚大厦B座403房
地址:广州市天河区广汕二路602号惠诚大厦B座403房
扫一扫 微信咨询
©2026 爱博能(广州)科学技术有限公司 版权所有 备案号:粤ICP备20046466号 技术支持:化工仪器网 Sitemap.xml 总访问量:103191 管理登陆